What is breast cancer?
Breast cancer is a disease where cells in the breast grow out of control. There are different types of cancer that develop in different parts of the breast.
There are three main parts of the breast: lobules, ducts, and connective tissue. Lobules are glands that produce milk, ducts are tubes that carry milk to the nipple, and connective tissue holds everything together. Most breast cancers begin in the ducts or lobules.

Who does breast cancer affect?
Most breast cancers (80%) occur in women over the age of 50, but younger women can get it too. Some transgender men and non-binary people can also be at risk.
About 1 in 8 women are diagnosed with breast cancer during their lifetime – it’s the most common cancer in the UK. But there’s a good chance of recovery if it’s detected at an early stage.
Signs and symptoms of breast cancer
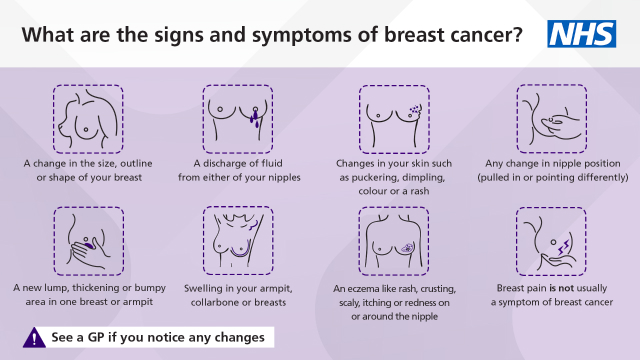

Signs and symptoms of Breast Cancer:
- A change in the size or shape of one or both breasts.
- A discharge of fluid from either of your nipples.
- A change in the look or feel of your skin, such as puckering or dimpling, a rash or redness.
- A change in the appearance of your nipple, such as becoming sunken into your breast.
- A new lump or area of thickened tissue in either breast that was not there before.
- A lump or swelling in either of your armpits.
- A rash (like eczema), crusting, scaly or itchy skin or redness on or around your nipple.
Further Information
For more information on breast cancer from the NHS click the link below.






